Vaccines to protect against Covid-19, the new coronavirus infection
Even though the pandemic is officially over, people around the world are still contracting Covid-19. The WHO and other health institutions are therefore advising at least certain population groups to receive booster vaccinations. There is also hope that in the future, vaccines will not only protect against a severe course of the disease, but even against infection, and ideally even with regard to different corona viruses. That is why companies and research institutes are continuing to work on corona vaccines.

Vaccination campaign in
Deeplink
This article remains permanently accessible via www.vfa.de/corona-vaccines.
In Germany, as in most EU countries, vaccination is carried out exclusively with Covid-19 vaccines, which have received marketing authorization from the EU Commission following review by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) (see figure below).
DOWNLOAD:
However, not all approved vaccines are in use or still in use in Germany. And in the fall of 2023, vaccines adapted to subtype XBB.1.5 will likely be the primary vaccines in use. Globally, other vaccines are also approved and in use for which no EU approval has been applied for. These include, for example, an mRNA vaccine from China and a DNA vaccine from India.
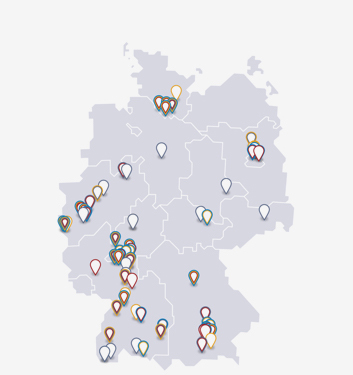
The following figure shows projects that are also explicitly working towards EU approval and for which at least testing with volunteers has already begun. Other such projects are still at the laboratory stage or at the stage of testing with animals.
Shown are companies and institutes whose Covid 19 vaccines have been ordered for the EU (flag) or are likely to be developed with the goal of EU approval (no claim to completeness). Shaded in gray: Variant-matched versions of previously approved vaccines (α = alpha, β = beta, o = omicron without subtype indication, BA.1 = omicron BA.1, BA.2 = omicron BA.2, BA.4/5 = omicron BA.4 and BA.5, XBB.1.5 = omicron XBB.1.5, w = wild-type). Influ. = vaccine is also intended to protect against influenza. D = DNA-based vaccine, I = inactivated pathogen vaccine, M = mRNA vaccine, Pe = peptide vaccine, Pr = protein-based vaccine, V = vector vaccine. If projects touch on Phase III and regulatory processes, part of the regulatory dossier has already been submitted and another is still pending (rolling review). Sources: EMA, EU Commission, vfa research; as of Sept. 02, 2023.
While some projects are still working on a first-generation vaccine, other companies and institutes are already working on second-generation vaccines that will provide even better protection against new SARS-CoV-2 variants or ensure that vaccinated individuals no longer transmit the virus, even symptom-free. This is explained in a separate article.
Development and production of Covid-19 vaccines in Germany
Numerous Covid-19 vaccine projects were initiated in Germany during the pandemic. But only one has produced an approved Covid 19 vaccine so far: the project by BioNTech and collaboration partner Pfizer for an mRNA vaccine. But projects for other vaccines are underway in Germany by the following companies and research institutions:
- CureVac (Tübingen) and GSK (UK): mRNA vaccines. Most advanced project in phase II.
- Speransa Therapeutics and Prime Vector Technologies (PVT) (Tübingen): Vector virus vaccines. Most advanced project in phase I.
- University of Tübingen: Peptide vaccine CoVac-1 specifically for patient:in cancer treatment or otherwise induced immunodeficiency. Project in phase II.
- Erlangen University Hospital: Vector vaccine for booster vaccinations to be administered as nasal or oral spray. Project in laboratory stage.
- University of Munich: Vector vaccine based on the MVA vector virus, which is expected to lead to an improved T-cell response, among other things. Status: n/a. A.
- The Free University of Berlin, the Universities of Bern and Geneva (Switzerland), the Friedrich Loeffler Institute, and RocketVax (Switzerland): Vaccine with attenuated (= attenuated) SARS-CoV-2 viruses for intranasal use. Status: preclinical development
- The consortium vir4vac from the University Hospital Tübingen and the Dept. of Molecular Medicine of the Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry in Martinsried: Vaccine of the type "semi-live vaccine". Status: n. A.
- Clinical Center of the LMU Munich: nasally administered vaccine with mRNA or DNA. The project is funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research. Status: Laboratory stage
- Ethris in collaboration with DIOSyn (UK), funded by CEPI: mRNA vaccine against covid-19 and other beta-coronaviruses. Status: Laboratory stage
In addition, the following companies and research institutes are involved in supporting vaccine production:
- Dermapharm (Brehna): participates in the production of the vaccine from BioNTech/Pfizer
- Allergopharma (Reinbek) participates in the production of the BioNTech/Pfizer vaccine (formulation step)
- Siegfried (Hameln): participates in filling and packaging of the vaccine from BioNTech/Pfizer and in future also from Novavax
- Sanofi (Frankfurt a.M.) participates in the filling of the vaccine from BioNTech/Pfizer
- Merck (Darmstadt, Germany) has contributed to about 50 Covid-19 vaccine development and production projects worldwide; the company also produces lipids for mRNA vaccines
- Lipoid: supplies phospholipids for the production of mRNA vaccines
- Evonik produces lipids for BioNTech/Pfizer's mRNA vaccine in Hanau and Dossenheim, Germany
Why a new vaccine (unlike a new version of an approved vaccine) cannot be developed without approved clinical trials was explained by immunologist Markus Löffler of the University Hospital of Tübingen on 23.03.2021 at Spiegel Online
Types of vaccines
Vaccines against covid-19 approved in the EU are based on mRNA, vector viruses, selected proteins, or killed coronaviruses. Other types have been approved in other regions; and more are in development. Here is an overview of the main vaccine types:
You can also download this chart as a PDF or as a JPG (free to use with attribution).
Protein-based vaccines: these are also called subunit vaccines and, according to some definitions (see below), are counted among the dead vaccines because they do not contain live viruses. These vaccines contain a few micrograms of a selected protein from SARS-CoV-2, but technically the protein is not derived directly from the coronavirus but is produced by genetic engineering. Examples include vaccines from Novavax (approved), Sanofi / GSK, and Texas Children's Hospital / Baylor College / Biological E (approved in India). Typically, vaccines with viral protein still contain an effect enhancer (adjuvant), which puts the immune system on alert immediately after vaccination. This makes it particularly alert to the injected foreign protein and builds up a defense against it; this can then also fight the actual viruses. Vaccines containing viral protein have already proved effective against other diseases, such as hepatitis B and influenza (in the latter case, however, the protein is usually obtained directly from the viruses).
mRNA vaccines: Instead of a selected viral protein, these vaccines contain the associated gene for it; and they do so in the form of an mRNA (messenger RNA) embedded in small vesicles (lipid nanoparticles) that protect them and allow them to enter cells. For cells, mRNAs are something commonplace; they constantly create mRNA transcripts of genes in the nucleus for themselves when they want to make the corresponding proteins. They use an externally supplied mRNA just as they would their own: they use it several times to make the protein described in it and then degrade it. In this way, viral protein is produced in the body after vaccination, which then activates the immune system in exactly the same way as vaccines with viral protein do (well illustrated by #EUmythbusters). mRNA vaccines have the advantage that the production process is always the same, regardless of the particular pathogen; thus, one saves development time for the production process. Two mRNA vaccines against Covid-19 are licensed in the EU (from BioNTech/Pfizer and from Moderna), plus several versions of these vaccines adapted to virus varieties. Other mRNA vaccines are licensed or under development in other regions of the world.
DNA vaccines: Similar to mRNA vaccines, DNA vaccines also work. In them, the gene for a viral protein is contained on a piece of DNA (for example, on a DNA ring [= plasmid]). After vaccination, the piece of DNA has to enter cells; and the cells then have to make transcripts from it into mRNA, which in turn is used to make viral protein, which then works as in a vaccine with viral protein. Thus, even more steps are required here to achieve the vaccine effect than with mRNA vaccines; and special inoculation devices are required for the DNA to enter the cells in the first place. One advantage over the mRNA vaccines approved to date, however, is that DNA is more stable and DNA vaccines therefore require less refrigeration. In India, the company Zydus has received approval for the first DNA vaccine against Covid-19, called ZyCoV-D (in fact, it is the world's first DNA vaccine ever); however, no EU approval has yet been applied for. In addition, Sweden's Karolinska Institute is also developing a DNA-based Covid-19 vacc ine and is currently testing it in a Phase I trial with volunteers.
Vector virus vaccines: As with mRNA and DNA vaccines, the aim of vector vaccines is to induce body cells to produce a SARS-CoV-2 protein by introducing a gene, which then stimulates a defense response in the immune system (1)
. However, the gene in question is introduced into the cells here with the help of another, harmless virus. Such harmless viruses, which are suitable as carriers, are called vector viruses. Examples are some adenoviruses from chimpanzees or gorillas and the "Modified Vaccinia Virus Ankara" (MVA). Vector vaccines against Covid-19 from AstraZeneca and Janssen are licensed in the EU. The Russian Gamaleya Institute's Sputnik V vaccine is under rolling review at the EMA. Other vector vaccines are in development, such as an inhalable vaccine by the German Center for Infection Research (DZIF) with IDT Biologika and a nasal vaccine by the University Hospital Erlangen. Prime Vector Technologies (Tübingen) and Speransa Therapeutics are also working on a vector vaccine. Even before the Corona pandemic, there were approved vector virus vaccines against Ebola.
Vaccines with inactivated SARS-CoV-2 viruses: such vaccines are based on one of the oldest principles of vaccine production: In principle, SARS-CoV-2 viruses themselves (produced in cell cultures) are used as vaccines to stimulate a protective immune response. The only difference is that they are previously damaged ("killed") in such a way that they are no longer capable of replication. This can be done with different techniques. Such vaccines are classified as inactivated vaccines by all the different definitions. One example is the EU-approved vaccine VLA2001 from Valneva.
Vaccines containing attenuated SARS-CoV-2 viruses: Attenuated viruses are viruses that can infect and replicate in humans, but only slowly. Thus, they cannot cause severe symptoms but can cause an immune response. Vaccines of this type have long been used against mumps, measles and rubella, among others. Now such vaccines are also being developed against Covid-19, among others by the Free University of Berlin in conjunction with the Universities of Bern and Geneva (Switzerland), the Friedrich Loeffler Institute, and RocketVax (Switzerland).
Peptide vaccines: Such vaccines are similar to vaccines containing viral protein - for example, they do not contain genetic material, but they do contain an effect enhancer (adjuvant). But instead of whole proteins, they contain only small fragments of them. These are particularly well suited to stimulating a protective defense response by T cells (a specific type of immune cell) after vaccination. This is of importance for people who cannot produce antibodies well due to cancer chemotherapy or congenital immunodeficiency and therefore rely on their T cells for a viral defense. No such vaccine has yet been approved in the EU, but the University of Tübingen (CoVac-1), among others, is working on it and has thus reached phase II.
Dead vaccines
The term "dead vaccines" is used inconsistently. Some understand it to mean only vaccines produced from killed pathogens. Others define the term more broadly, such as the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) or the Robert Koch Institute. In the table below, a distinction is made between mRNA vaccines, vector virus vaccines, DNA vaccines, protein-based vaccines, peptide vaccines and vaccines with inactivated pathogens (= SARS-CoV-2). The BMBF definition of inactivated vaccines includes the last three categories, while the RKI also includes mRNA and vector virus vaccines.
Forms of application
There are also differences in the forms of application. Although most projects are aimed at injectable vaccines, there are exceptions. For example, the development of vaccines that can be administered via the nose is linked to the hope of immunizing people in such a way that they are not only protected against an outbreak of the disease themselves, but also that they can no longer infect anyone else with SARS-CoV-2. One of these projects is being pursued by the University Hospital Erlangen (see above). Animal experiments have been positive. More on this topic can be found in the article"Next generation corona vaccines".
Footnotes
(1) mRNA, DNA and vector vaccines are therefore sometimes combined to form "gene-based vaccines"